Introduction
Reprogramming Microbial Realities: My Journey in Engineering the Invisible
I have over 26 years (since June 1999) of diverse work experience in computer systems, inverse problems, medical imaging, and, more recently, microbial informatics. I have led transformative research projects internationally - from pioneering diagnostic imaging algorithms to developing cutting-edge bioinformatics tools and driving sustainable solutions in agriculture, aquaculture, water treatment, and public health. Through my work, I not only push the boundaries of science but also actively contribute to global initiatives such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs), which provide a framework for ensuring a healthier, more equitable, and sustainable future.From Inverse Problems to Biological Insight
My early career was characterised by a deep engagement with inverse problems - challenging mathematical techniques that require reconstructing hidden parameters from observable data. At Jeju National University, South Korea and later at University of Cambridge, I worked tirelessly on dynamic imaging techniques using electrical impedance tomography and advanced 3D ultrasound systems. I vividly recall the breakthrough moments, such as developing a novel Kalman-filter based reconstruction method (DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/19/6/065501) and devising dynamic flow measurement techniques (DOI: 10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2006.12.005). These studies - further led to exploring advances in 3D ultrasound imaging reliability (DOI: 10.7863/ultra.32.4.699) and clinical validations (DOI: 10.1259/bjr/46007369) - provided the quantitative rigor that has shaped my approach to all subsequent research.Embracing Microbial Ecology: Unveiling the Hidden World
The advent of high-throughput sequencing in the early 2010s revolutionized our ability to study the microbial world. I found myself irresistibly drawn to understanding the dynamic complexity of microbial communities. How do these unseen organisms assemble, adapt, and thrive under fluctuating environmental conditions? I explored ecological null models and taxa-centric analyses to address these questions. My research in this area, including studies that outline statistical frameworks for community assembly (DOI: 10.1002/ece3.8091) and explore microbial resilience (DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1197838), has not only advanced scientific understanding but also has far-reaching implications for environmental management - directly supporting UN SDG 13 (Climate Action) and UN SDG 15 (Life on Land).Transforming Theory into Tools: Democratizing Discovery in Microbial Informatics
I have always believed that breakthrough science should be accessible. My commitment to transforming theory into practical tools led me to contribute to a suite of innovative bioinformatics software. One highlight is CONCOCT (DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3103), a genome binning tool for metagenomic assemblies that contributed to the discovery of the novel Commamox lineage (DOI: 10.1126/science.aad9839). Equally groundbreaking is SEQENV, a text-mining engine that links genomic sequences to environmental contexts using Environmental Ontology (DOI: 10.7717/peerj.2690; DOI: 10.7717/peerj.3827). My suite further expands with microbiomeSEQ (an R package for microbial community analysis in an environmental context; DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.17108.71047), NanoAmpli-Seq (a workflow for amplicon sequencing from mixed microbial communities on Oxford Nanopore; DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giy140), PyTag (a software facilitating systematic reviews using prevalent ontologies; DOI: 10.7287/10.7717/peerj.5047), and CViewer (a Java software for multivariate statistical analysis of shotgun metagenomics datasets with other omics modalities; DOI: 10.1186/s40168-024-01834-9). I have also significantly contributed to RVLAB (an online statistical processing environment for multivariate analysis of microbial communities; DOI: 10.3897/BDJ.4.e8357), and NMGS (a software for fitting unified theory of neutral models to microbial communities; DOI: 10.1109/JPROC.2015.2428213). By making such tools open-source, I support UN SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) and UN SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals) by enabling global collaboration and empowering researchers everywhere.Integrating Data: Crafting a Multi-Dimensional View of Life
Understanding the complexity of life requires merging diverse data streams into a coherent narrative. I have led efforts to integrate microbiome data with metabolomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic profiles using advanced latent variable models and multi-omics methodologies. Such integrative approaches - detailed in publications like DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1930871, DOI: 10.1039/C9FD00020H, and DOI: 10.3389/fsysb.2024.1432791 - provide a panoramic view of how microbial interactions influence cellular function and overall ecosystem health. This work has profound implications for UN SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-Being) and UN SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), by linking molecular details to systemic outcomes.Revolutionizing Agriculture and Aquaculture: The Microbial Edge
A major challenge in developing sustainable approaches to agriculture is a lack of fundamental understanding about what allows some plants to adapt better than others to pressures arising from changes in both the biotic and abiotic environments. In the face of the current climate emergency, it will become critical to design crops that will be resilient to the environmental variability resulting from the increasing unpredictability and extremes of local weather during the growing season. However, if we are to achieve long-term sustainable solutions to food security, we also need to move beyond management of single crop species and consider impacts on overall ecosystem health and biodiversity. This is not only important for conservation but will in turn help to simultaneously improve yields of multiple crop species. Moreover, such changes in management practices will only translate into increased food security if they are economically viable: if consumers, supermarkets and growers are willing to engage with a change to more sustainable food sources. My significant contributions in the leading role are as follows: (a) With James Hutton Institute: Centre for Sustainable Cropping (CSC), I am integrating existing data (13 years, to-date the most extensive and long-standing trial in the UK) to quantify fluctuations across space and time in both the abiotic and biotic environments in relation to sustainable vs traditional conventional cropping of different potato varieties. This work builds on the main outcome of a £2M BBSRC UKRI Strategic Priorities Fund - Bacterial Plant Diseases BB/T010657/1, Building a Decision Support Tool for Potato Blackleg Disease (DeS-BL) grant (DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.19.545554); (b) With Forman Christian College (A chartered University), Lahore, Pakistan, we have successfully demonstrated how to suppress Cotton Leaf Curl Disease (CLCuD) by application of Salicylic Acid producing bacteria (DOI: 10.1007/s00284-024-03827-1; DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1381883; DOI: 10.1038/s41522-023-00470-9), and through interspecies microbiome transplantation (DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-07812-7). A recent press release, "Microbiota transplantation offers new hope against cotton leaf curl disease", highlights the importance of this work for sustainable agriculture. CLCuD is transmitted by the whitefly Bemisia tabaci, and has devastated Pakistan’s cotton crop for the past three decades with economic losses reaching approximately 2 billion USD per annum in Pakistan. We are currently undertaking on-field trials in Pakistan. All of these works are paving the way toward sustainable, non-chemical plant protection strategies that support UN SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) and UN SDG 15 (Life on Land).The global demand for food and protein continues to rise as the world’s population is set to hit 9.7 Billion by 2050. Reducing demands on meat protein and increasing fish consumption is good for our health and potentially more environmentally sustainable. Fish consumption has already eclipsed beef consumption globally. Aquaculture production of fish is a booming industry that could eventually satisfy global fish food demands and reduce our reliance on wild resources. However, for some fish species, such as the Atlantic cod, capture fishing remains the dominant means of production (>97%). As a result, many cod stocks are in decline. Consequently, the farming of cod could offer a sustainable and reliable means to meet consumer demand for seafood. In a series of papers directed by me (DOI: 10.1038/s41522-022-00296-x; DOI: 10.1186/s42523-020-00065-1), we have demonstrated the impact of diet supplementation of juvenile Atlantic cod with seaweeds (macroalgae; egg wrack [Ascophyllum nodosum] or sea lettuce [Ulva rigida]) in a typical farming setting. Our work sheds valuable insights into what ecological processes drive the hindgut microbiome in juvenile Atlantic cod. With the advent of novel functional feed supplements from the biotech industries we will need to explore how these additives can benefit farmed fish species like salmon, trout and marine species such as seabass and bream with a view towards producing robust healthy fish for the consumer. Our approach opens the door to a better understanding of these possibilities. As an outreach exercise, we were invited to write a blogpost on Nature Communities, "How do microbial communities assemble in the gut of Atlantic cod in response to diet and novel ingredients?".
In aquaculture, the development of the SalmoSim simulator to replicate the gut microbiome of Atlantic salmon, as well as exploring microbial ecology of Atlantic Salmon (DOI: 10.1186/s40168-021-01134-6; DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01953-21; DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736772; DOI: 10.1038/s41522-022-00296-x; DOI: 10.1186/s42523-020-00065-1; DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17008-2) represents another breakthrough. This enhances our understanding of fish nutrition and health, contributing directly to the sustainability of global seafood supplies.
The factors affecting host-pathogen ecology in terms of the microbiome remain poorly studied. Chickens are a key source of protein with gut health heavily dependent on the complex microbiome which has key roles in nutrient assimilation and vitamin and amino acid biosynthesis. The chicken gut microbiome may be influenced by extrinsic production system parameters such as Placement Birds/m2 (stocking density), feed type and additives. With MoyPark (UK’s largest producer of organic and free range chicken, and one of the the UK’s top 15 food companies), three papers on chicken microbiomes (DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02452; DOI: 10.1186/s40168-020-00908-8; DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1197838) have led to exploring the diet and their industrial parameters to help control the pathogen Campylobacter, resulting in a press release by Agri-Food & Biosciences Institute, UK Government ("High impact research paper published in Journal of Microbiome"). My current work with MoyPark is towards Alternatives To Antibiotics (ATAs) that can be utilised in animal production for maintenance of gut health, reduction of pathogen load, and improved feed efficiencies (DOI: 10.1101/2024.08.02.606333). Similarly, with National Veterinary Laboratory (NVL), Pakistan (Ministry of National Food Security & Research, Pakistan), I am taking a leading role in understanding the microbial ecology of local/indigenous breeds, improving commercial and backyard farming setups in Pakistan, and reducing antimicrobial resistance (DOI: 10.1186/s13104-025-07220-4; DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2024.110552; DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2024.110487; DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1197838).
Pioneering Water, Wastewater, and Environmental Technologies
I have a significant portfolio in leading and directing research on water and waste-water treatment. Majority of the work is in collaboration with University of Galway, Ireland where I have held a visiting lectureship and where I supervise students and postdocs. My most impactful work has been on understanding Anaerobic Digestion (AD) processes. In the natural environment, organic matter is degraded by diverse communities of microorganisms through AD which can be harnessed for engineered wastewater treatment. Compared to conventional treatment processes, AD is less energy-intensive, reduces land-use requirements, and produces biogas as a renewable energy source. AD is a biological process, reliant on the livelihood and activity of the microbial communities ‘eating’ the organic pollutants. If the bacteria are unable to survive, the system fails. Generally, microorganisms thrive at warm temperatures (around 37°C), but heating wastewater requires significant energy expenditure, especially in temperate climates. In a series of paper below we have shown that we could train or adapt the microbial community to operate at low temperatures with such adaptations would avoid the costs and energy consumption associated with heating, creating meaningful change for the way wastewater is treated in colder climates. My recent work includes: first evidence for temperature influencing the enrichment, assembly and activity of polyhydroxyalkanoate-synthesizing mixed microbial communities (DOI: 10.3389/fsysb.2024.1375472); intI gene abundance as a proxy for antimicrobial resistance (DOI: 10.1128/aem.01071-23); understanding microbial ecology in drinking water treatment and distribution systems (DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118106); low temperature AD applications (DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162420; DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126098); understanding sulfur-driven denitrification performance and microbial community dynamics (DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131975); understanding microbial electrosynthesis (DOI: 10.1038/s41522-022-00337-5); understanding granules microbiology and why granules float in AD reactors (DOI: 10.1128/Spectrum.00784-21; DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.666584; DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112229; DOI: 10.1128/mSystems.00323-20; DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01126); and improving protocols for microbial community detection (DOI: 10.1186/s40168-018-0449-9).Additionally, my work on employing Rhamnolipid as a biodegradable biosurfactant for oil spill remediation (DOI: 10.1186/s40168-021-01143-5) showcases the transformative potential of microbe-based technologies in environmental crises, aligning with UN SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and UN SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities). The biosurfactant did not suppress the oil-eating bacteria, so more of the aromatic hydrocarbons were degraded when it was used. This is summarised in a video abstract associated with our project and entitled, "Rhamnolipid, a naturally produced oil dispersant, may improve oil spill remediation". The study has environmental impact as ascertained by a press release by Heriot-Watt University, entitled "Oil industry should invest in bio solutions for oil spills".
Microbiomes, Health, and Social Equity: Decoding the Invisible Determinants
The interplay between our microbial communities and our health is profound. I have engaged in extensive collaborations to study how factors such as sanitation, diet, antibiotic use, and socioeconomic status shape the human microbiome. Findings from these studies are pivotal for addressing antimicrobial resistance and chronic diseases while informing public health policy, critical for UN SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-Being). Impactful works in this area include:- Investigating anthropometric, sociodemographic, and dietary patterns and their impact on gut microbial communities (DOI: 10.1186/s13099-024-00596-x).
- Exploring microbiota of those who have stunted growth (DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-32491-x).
- Exploring the "diseasome of ageing" (DOI: 10.1042/CS20230779).
- Socioeconomic position linked to circulatory microbiota differences with biological age (DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-92042-0). This work is covered in the national press (such as The Times): "Unfriendly gut bacteria linked to early ageing".
- Effect of smoking on human pharynx microbiota and composition (DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02166-21) as well as those who have Streptococcus pneumoniae colonoization (DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-4215-3).
- Exploring insights into the systemic cytokine signature associated with Alopecia areata (DOI: 10.1111/bjd.18008).
- Exploring an ancient clay remedy that may have potential to boost modern gut health, also covered in national media (The Times and Newsweek): "Ancient Pill Secret From 2,500 Years Ago May Improve Gut Health".
- Exploring treatment responses on microbiota and immunophenotype, particularly in view of Psoriatic Arthritis (DOI: 10.1101/2023.05.18.2328997), Multiple Sclerosis (DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-74975-4), Human Type 2 Diabetes (DOI: 10.1017/S0007114516004086), and Parkinson's disease (DOI: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.01.005).
- Exploring inter-kingdom relationships in diseases where microbial dysbiosis is implicated, and their metabolic consequences (DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1930871).
- Exploring endemic fluorosis when individuals are living in a region characterised by elevated levels of fluorine in the drinking water, food, and/or air (DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116959).
- Timely understanding and curtailing the spread of Anti Microbial Resistance (AMR) bacteria, determining the load of AMR pathogens and associated resistance patterns not only within clinical setups but also environment and companion/livestock animals since majority rural households are engaged in agriculture (DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11020279; DOI: 10.1186/s13104-025-07220-4).
- Exploring dietary interventions such as CD-Treat Diet (DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.12.002), BIOPIC Diet for treatment for cases with active Crohn’s Disease (CD). Some of these are part of open-label trial at NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde in CD patients with active disease, instead of using their standard medical treatment.
- Exploring Gluton-Free Diet (DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.08.007) and their alterations in intestinal microbiota of children with Celiac Disease.
Revisiting Early Contributions: The Power of Inverse Problems
Before my pivot to microbial informatics, my work in inverse problems provided the analytical bedrock for all that followed. During my PhD (published >40 papers), I focused primarily on the development of static and dynamic algorithms for Inverse Problems that arise in a wide range of engineering areas and worked mainly on Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT), Electrical Capacitance Tomography (ECT), Mobile Ad hoc Network (MANET), Global Positioning System (GPS), and Inverse Heat Conduction Problem. I have developed novel tomographic imaging methods using EIT and ECT to manipulate measurement data from electrodes attached to the surface of a pipeline in order to estimate the multidimensional distribution of physical parameters inside. As compared to the traditional EIT and ECT, I have considered the scenarios in which the object to be imaged is changing very rapidly during the data acquisition; necessitating a desire for reasonable spatio-temporal resolution. Rather than considering the inverse problem as a traditional tomography reconstruction problem, the problem was formulated as a state estimation problem utilising different kinematic evolution models for the physical parameters along with an observation model based on Finite Element Method (FEM). In particular, I have developed Kalman-type inverse algorithms for: estimation of the concentration distribution by the convection-diffusion equation that allowed for approximation of the velocity field (DOI: 10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2006.12.005); estimation of time-varying interfacial boundary in stratified flows of immiscible liquids (DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/19/6/065501; DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/18/5/012, targeting liquid hydrocarbon transportation in pipelines that often contain free water); imaging of a stirrer vessel for detection of air distribution and detection of air bubbles (DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/21/3/035501; DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.12.025; DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/18/1/008); estimation of settling curves and velocities in the sedimentation process for different layers under the influence of gravity (DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2009.0081, targeting industrial applications such as mining, waste water treatment, and the pulp and paper industry); and visualisation of two-phase flow through rod bundles in nuclear power plants (DOI: 10.1063/1.2747522). These works, though focused on the intricacies of inverse problems, instilled in me the rigorous analytical approach that has been the hallmark of my subsequent research.Revisiting Early Contributions: Improving Medical Imaging (Computer Vision)
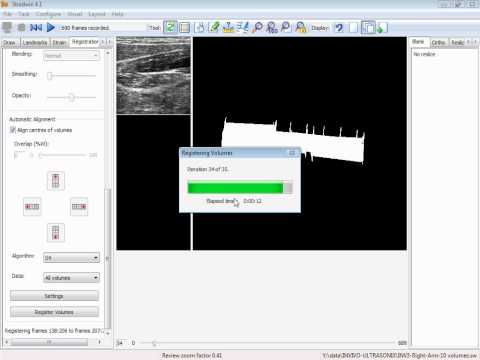
Between 2008 and 2011, I worked as a Post-doc in the University of Cambridge and developed a Hybrid 3D Ultrasound Imaging System. The project focused on: tracking the trajectory of a 3D ultrasound probe based on the image-based registration of acquired data and the output of an inertial position sensor (DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/21/8/085803; DOI: 10.1243/09544119JEIM586); calibration of the hybrid system; correction of artifacts in the data caused by variations of the pressure from the probe during the scan; differentiation of backscatter into diffuse and directional components using the overlap data from multiple scans (DOI: 10.7863/ultra.32.4.699); and development and evaluation of software tools to enable the system to be used effectively in a hospital environment (DOI: 10.1259/bjr/46007369). The developed system was then shipped to Addenbrookes’ Hospital, Cambridge, where after successfully completing the review by the ethics committee, a clinician explored the range of applications in which such type of a 3D scanner could offer potential benefits. As a proof-of-concept, we carried out a feasibility study recruiting pregnant women attending for routine obstetric ultrasound scans and have obtained promising results (77% to 83% reliability of overlapping scans in clinical trials; DOI: 10.1259/bjr/46007369).Revisiting Early Contributions: Network Inference
Between 2011 and 2012, I worked as a Senior Post-Doc in the University of Oxford. I scoped a form of dashboard that gives policy makers an integrated view of the state of the UK, both at the current time, and into the past. If we are equipped with a better view of the UK, we can ensure that it is more resilient to shocks. I investigated methods to infer time-varying networks from multiple time signals. The time signals pertain to Google trends, Twitter feeds, stock prices, exchange rates, commodity prices, weather statistics and transport statistics. This project resulted in GlobalView, a software tool for finding both directed and undirected relationships between time signals.Revisiting Early Contributions: Transition towards understanding biological systems
From 2005 to 2006, I worked on a joint project with the Systems Biology Group at Jeju National University and developed a software, 2D electrophoresis Gel Image Processor for Matlab (DOI: 10.1109/FBIT.2007.95). This software is useful for the analysis of bio-markers by quantifying individual proteins, showing the separation between one or more protein "spots" on a scanned image of a 2D gel, and measuring running differences between several gel images.What began as a technical challenge - writing image processing algorithms and building analytical tools - soon became something much more meaningful. Immersed in the biological questions driving the project, I found myself increasingly drawn to the science behind the data. This experience marked a pivotal shift in my career trajectory: it was the first time I saw how computational tools could unlock insights into complex biological systems. Working at the interface of engineering and biology, I realized I wanted to move beyond writing code for biology to actually becoming a biologist - someone who could ask the scientific questions, not just support them technically. This project became the bridge that carried me from engineering into the life sciences, reshaping both my professional identity and long-term goals.

 orcid.org/0000-0001-5780-8551
orcid.org/0000-0001-5780-8551 (similar to modern day Google). Launched back in
(similar to modern day Google). Launched back in